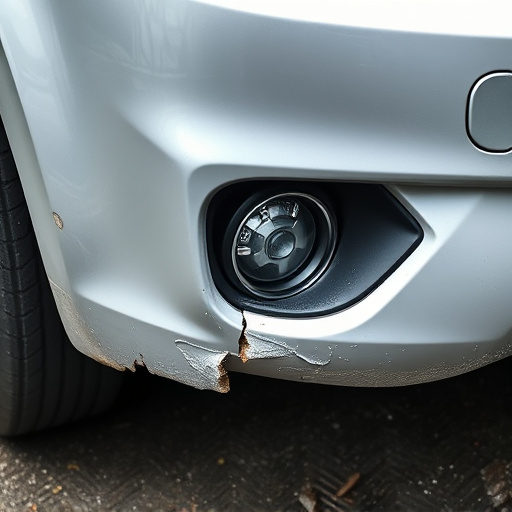
Core Support Replacement (CSR), a critical process in auto collision repair, involves repairing and reinstalling damaged core components for enhanced structural integrity, performance, and vehicle lifespan. Adhering to legal compliance requires navigating complex regulations on material sourcing, disposal, and worker safety. Best practices include meticulous record-keeping, staff training, staying current with industry standards, effective waste management, and recycling programs. Implementing CSR demands a strategic approach involving an assessment of current systems, staff training, open communication, and feedback to ensure smooth transition without compromising safety or service quality.
“In an era driven by technological advancements, understanding core support replacement is no longer a niche concern but a strategic imperative. This article serves as your comprehensive guide through the complex landscape of core support replacement, focusing on its definition, objectives, and the legal compliance requirements that shape its implementation. From defining key terms to exploring best practices and successful transition strategies, we demystify this process, empowering organizations to navigate the legal aspects effectively.”
- Understanding Core Support Replacement: Definition and Objectives
- Legal Aspects: Compliance Requirements and Best Practices
- Implementing Core Support Replacement: Strategies for Successful Transition
Understanding Core Support Replacement: Definition and Objectives

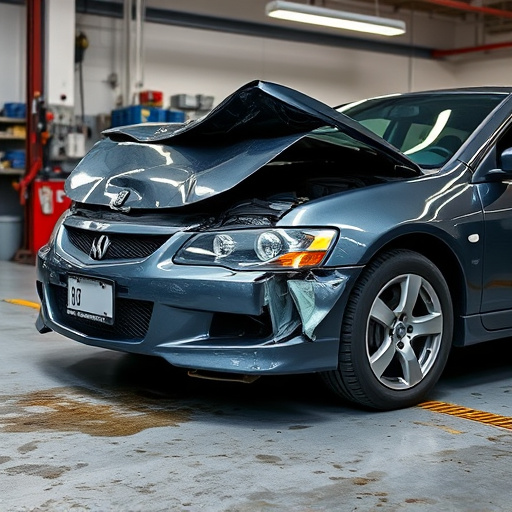
Core Support Replacement (CSR) is a critical process within the automotive industry, focusing on the efficient and effective replacement of damaged or worn-out core components in vehicles. This procedure involves meticulous disassembly, repair, and reinstallation of essential parts, ensuring the vehicle’s structural integrity and safety. The primary objectives of CSR are to restore the vehicle to its original condition, enhance performance, and extend the lifespan of the affected areas, specifically in auto body repair scenarios.
In the context of auto collision repair, CSR plays a pivotal role in mitigating costs and reducing downtime for vehicle owners. By addressing core support issues, technicians can prevent further damage and ensure the overall quality of the repair. This meticulous process requires specialized knowledge and equipment, often involving advanced techniques like precision welding and state-of-the-art painting to match the vehicle’s original finish, such as in vehicle paint repair applications.
Legal Aspects: Compliance Requirements and Best Practices

In the realm of core support replacement, understanding legal compliance requirements is paramount for any auto collision center or vehicle repair shop. These regulations are designed to ensure safety, quality, and ethical practices in the automotive industry. When conducting core support replacement, businesses must adhere to local, state, and federal guidelines that govern material sourcing, disposal methods, and worker safety protocols. Failure to comply can lead to significant legal consequences, including fines and reputational damage.
Best practices for legal compliance involve maintaining comprehensive records of all materials used, ensuring proper training for staff involved in core support replacement, and staying updated on evolving industry standards. Additionally, establishing robust internal processes for waste management and recycling can further mitigate legal risks. By prioritizing these measures, auto repair shops not only safeguard themselves from legal repercussions but also contribute to sustainable vehicle repair practices, enhancing their reputation as responsible members of the community.
Implementing Core Support Replacement: Strategies for Successful Transition

Implementing Core Support Replacement requires a strategic approach for a successful transition. The first step is to assess the current system and identify areas that need updating. This involves evaluating the efficiency, effectiveness, and reliability of existing core support components, as well as their compatibility with modern vehicle models and repair trends. By thoroughly understanding these aspects, businesses can make informed decisions about which replacement parts and technologies best suit their operations, ensuring a seamless shift without compromising quality or safety standards.
A key strategy during the transition is training staff on new systems and procedures related to core support replacement. This includes educating technicians on any changes in collision repair services, vehicle repair services, or auto detailing processes required for the updated components. Adequate training empowers employees to handle the new equipment competently, maintain high standards of work, and contribute to a smooth transition period. Additionally, establishing clear communication channels among team members and fostering an environment open to feedback can help address any challenges that arise during the implementation process.
Core support replacement is not just a technical update but a strategic initiative that demands careful navigation through legal compliance requirements. By understanding the definition and objectives of this process, organisations can effectively implement best practices and successful transition strategies. Staying compliant with relevant laws and regulations ensures minimal disruption to business operations while maximising the benefits of core support replacement, ultimately driving digital transformation and competitiveness in today’s market.